References
The bhaptics_python module provides functions for controlling bHaptics haptic devices from Python. It enables you to play haptic patterns, control device motors directly, and manage haptic playback.
import bhaptics_python
Play Event-driven Haptic
Play haptic patterns bound to specific events (designed in the bHaptics Designer/Portal). These are the recommended functions for most applications.
play_event
async def bhaptics_python.play_event(event_name: str) -> int
async def bhaptics_python.play_event(event_name: str, device_index: int) -> int
Play the predefined haptic event.
- Playing events affects the haptic devices which device index is default(
-1). Simply use the first parameter —event name— only. This can be used in general purposes. - If you want to actuate the specific haptic device, you can also use the second parameter —device index—. You can check or set the device index in the bHaptics Player.
Parameters
event_name: Name of the haptic event.device_index(optional): Device index of the haptic device.
Returns
Request ID. You can use this to stop playback. Returns -1 if failed.
Example
import bhaptics_python
async def play_example():
request_id = await bhaptics_python.play_event("heartbeat")
print(f"Playback request ID: {request_id}")
play_param
async def bhaptics_python.play_param(
event_name: str,
intensity: float,
duration: float,
x_offset: float,
y_offset: float
) -> int
async def bhaptics_python.play_param(
event_name: str,
intensity: float,
duration: float,
x_offset: float,
y_offset: float,
device_index: int
) -> int
Play the haptic event, with adjusting the strength, duration, and direction of the haptic.
Parameters
event_name: Name of the haptic event.intensity: Multiplier for haptic intensity. Valid range is: [0.0-2.0] (Default:1.0)duration: Multiplier for duration. (Default:1.0)x_offset: Rotate haptic counterclockwise. Valid range is: [0.0-360.0] (Default:0.0)y_offset: Move haptic up or down. Valid range is: [-0.5-0.5] (Default:0.0)device_index(optional): Device index of the haptic device.
Returns
Request ID. You can use this to stop playback. Returns -1 if failed.
Example
import bhaptics_python
async def play_params_example():
request_id = await bhaptics_python.play_param(
"pistol_r", 5.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0
)
play_loop
async def play_loop(
event_name: str,
intensity: float,
duration: float,
x_offset: float,
y_offset: float,
interval: int,
max_count: int
) -> int
async def play_loop(
event_name: str,
intensity: float,
duration: float,
x_offset: float,
y_offset: float,
interval: int,
max_count: int,
device_index: int
) -> int
Plays haptic events in a loop.
Parameters
event_name: Name of the haptic event.intensity: Multiplier for haptic intensity. Valid range is: [0.0-10.0] (Default:1.0)duration: Multiplier for duration. (Default:1.0)x_offset: Rotate haptic counterclockwise. Valid range is: [0.0-360.0] (Default:0.0)y_offset: Move haptic up or down. Valid range is: [-0.5-0.5] (Default:0.0)interval: Time interval between loops, in milliseconds.max_count: Number of loops.device_index(optional): Device index of the haptic device.
Returns
Request ID. You can use this to stop playback. Returns -1 if failed.
Example
import bhaptics_python
async def play_loop_example():
result = await bhaptics_python.play_loop(
"heartbeat", 0.8, 1000, 90, 0, 150, 5
)
play_without_result
async def bhaptics_python.play_without_result(
event_name: str,
intensity: float,
duration: float,
x_offset: float,
y_offset: float
)
async def bhaptics_python.play_without_result(
event_name: str,
intensity: float,
duration: float,
x_offset: float,
y_offset: float,
device_index: int
)
Plays haptic events without waiting for results (fire-and-forget).
Parameters
event_name: Name of the haptic event.intensity: Multiplier for haptic intensity. Valid range is: [0.0-10.0] (Default:1.0)duration: Multiplier for duration. (Default:1.0)x_offset: Rotate haptic counterclockwise. Valid range is: [0.0-360.0] (Default:0.0)y_offset: Move haptic up or down. Valid range is: [-0.5-0.5] (Default:0.0)device_index(optional): Device index of the haptic device.
Example
import bhaptics_python
async def play_without_result_example():
await bhaptics_python.play_without_result(
"heartbeat", 0.8, 1.0, 90, 0.25
)
Play Haptic Directly
If you want to play haptics without events, use these functions.
play_dot
async def bhaptics_python.play_dot(
position: int,
duration_millis: int,
values: list[int]
) -> int
async def bhaptics_python.play_dot(
position: int,
duration_millis: int,
values: list[int],
device_index: int
) -> int
Play haptic feedback on the specific haptic actuator.
Parameters
position: Type of haptic device to playback.Value Device 0TactSuit 1TactSleeve(Left) 2TactSleeve(Right) 3TactVisor 4Tactosy for Hands(Left) 5Tactosy for Hands(Right) 6Tactosy for Feet(Left) 7Tactosy for Feet(Right) 8TactGlove(Left) 9TactGlove(Right) duration_millis: The duration of haptic, measured in millisecond. Greater than or equal to100is recommended.values: Assign the length of the list by the number of motors for device. Values in the list means motors' intensity. Valid range for each value in the list is: [0-100]device_index(optional): Device index of the haptic device.
Example
import bhaptics_python
async def play_dot_example():
# Sequentially activate 32 motors
motor_len = 32
values = [0 for _ in range(motor_len)]
for i in range(motor_len):
values[i] = 50
if i > 0:
values[i - 1] = 0
request_id = await bhaptics_python.play_dot(0, 500, values)
time.sleep(0.5)
play_path
async def bhaptics_python.play_path(
position: int,
duration_millis: int,
x: list[float],
y: list[float],
intensity: list[int]
) -> int
async def bhaptics_python.play_path(
position: int,
duration_millis: int,
x: list[float],
y: list[float],
intensity: list[int],
device_index: int
) -> int
Play haptic around specific coordinates. Unlike play_dot function, which specifies the haptic intensity for each haptic actuator individually, this method specify the haptic intensity for particular coordinates.
When specifying haptic position, play_dot offers discrete control, while play_path is more continuous. play_dot assigns intensity to individual actuators, whereas play_path allows intensity specification for specific coordinates (between 0 and 1 for both X and Y axis), causing nearby actuators to vibrate accordingly.
You can put multiple coordinates with multiple intensities. Note that all actuators around these coordinates in the list will activate simultaneously (at the same time), not sequentially. Moreover, the size of all lists must be the same.
By continuously calling this function while gradually changing the values, you can achieve the effect of a moving haptic point.
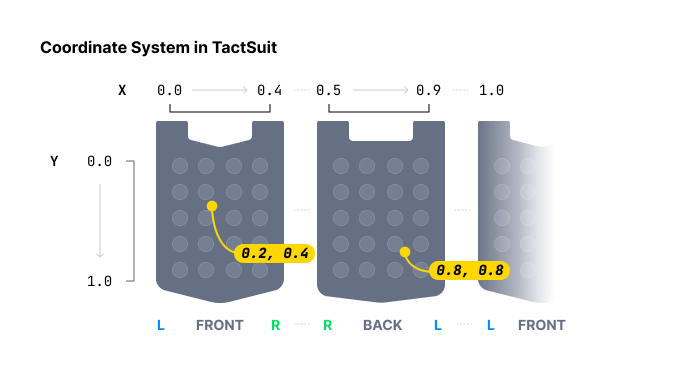
Parameters
position: Type of haptic device to playback. For more information, please refer here.Value Device Motors Count 0TactSuit 32 1TactSleeve(Left) 3 2TactSleeve(Right) 3 3TactVisor 4 4Tactosy for Hands(Left) 6 5Tactosy for Hands(Right) 6 6Tactosy for Feet(Left) 6 7Tactosy for Feet(Right) 6 8TactGlove(Left) 6 9TactGlove(Right) 6 duration_millis: The duration of haptic, measured in millisecond. Greater than or equal to100is recommended.x: List of X coordinates for the haptic effect. Each value must be in the range: [0.0-1.0]y: List of Y coordinates for the haptic effect. Each value must be in the range: [0.0-1.0]intensity: List of intensity values for each coordinate. The length must match the number of coordinates. Each value must be in the range: [0-100]device_index(optional): Device index of the haptic device.
Example
import bhaptics_python
import time
async def play_path_example():
# Path of point #1
x1 = [0.738, 0.723, 0.709, 0.696, 0.682, 0.667, 0.653]
y1 = [0.680, 0.715, 0.749, 0.782, 0.816, 0.852, 0.885]
intensity1 = [20] * len(x1)
# Path of point #2
x2 = [0.061, 0.072, 0.102, 0.184, 0.254, 0.310, 0.363]
y2 = [0.632, 0.587, 0.542, 0.498, 0.411, 0.366, 0.301]
intensity2 = [60] * len(x2)
for i in range(len(x1)):
# Point #1 and #2 will vibrate at the same time.
await bhaptics_python.play_path(0, 250, [x1[i], x2[i]], [y1[i], y2[i]], [intensity1[i], intensity2[i]])
time.sleep(0.25)
play_glove
async def bhaptics_python.play_glove(
position: int,
motors: list[int],
playtimes: list[int],
shapes: list[int],
repeat_count: int
) -> int
TactGlove Only. Play haptics in TactGlove. Unlike using play_dot, you can finely adjust haptic duration and vibration intensity changes. This allows for even more detailed expression of haptic feedback.
Each list must have six elements, and at least one element is required to work.
Parameters
-
position: Type of haptic device to playback. Use8or9only.Value Device 8TactGlove(Left) 9TactGlove(Right) -
motors: A list consisting of six elements, each representing the intensity of a motor. The list must have a length of six, as there are six motors in one TactGlove. Valid range for each value in the list is: [0-100] -
playtimes: A list consisting of six elements, each representing a time interval for actuation.Value Playtimes 15ms 210ms 420ms 630ms 840ms -
shapes: A list consisting of six elements, each representing the forms of haptic intensity changes over time.Value Waveform 0Constant intensity for the duration 1Starts at the specified intensity and decreases by half 2Starts at half of the specified intensity and increases to the specified one. -
repeat_count: Number of repetitions.
Example
import bhaptics_python
import time
async def play_glove_example():
motors = [100] * 6
playtimes = [8] * 6
shapes = [2] * 6
# Left hand
for _ in range(3):
await bhaptics_python.play_glove(8, motors, playtimes, shapes, 0)
time.sleep(0.3)
# Right hand
for _ in range(3):
await bhaptics_python.play_glove(9, motors, playtimes, shapes, 0)
time.sleep(0.3)
Playback Control
stop_by_request_id
async def bhaptics_python.stop_by_request_id(request_id: int)
Stop haptic playback by request ID.
Parameters
request_id: Request ID returned by the haptic playing function.
Example
import bhaptics_python
import asyncio
async def stop_by_id_example():
request_id = await bhaptics_python.play_event("shoot")
await asyncio.sleep(2)
await bhaptics_python.stop_by_request_id(request_id)
stop_by_event_name
async def bhaptics_python.stop_by_event_name(event_name: str)
Stop all haptic playback for a specific event name.
Parameters
event_name: Name of the haptic event you want to stop.
Example
import bhaptics_python
import asyncio
async def stop_by_name_example():
await bhaptics_python.play_event("shoot")
await asyncio.sleep(2)
await bhaptics_python.stop_by_event_name("shoot")
stop_all
async def bhaptics_python.stop_all()
Stop all haptic currently playing.
Lifecycle
registry_and_initialize
async def bhaptics_python.registry_and_initialize(
app_id: str,
api_key: str,
app_name: str
) -> bool
Initialize the haptic environment. It will initialize the SDK and establishes connection with bHaptics Player. This function should be called before using the haptic-related functions.
Parameters
app_id: Application ID created in bHaptics Developer Portal.api_key: API key created in bHaptics Developer Portal.app_name: Application name you want. Or you can just put the empty string("").
Returns
Initialization success status.
Example
import bhaptics_python
import asyncio
async def main():
app_id = "your_app_id" # App ID created in bHaptics Developer Portal
api_key = "your_api_key" # API key created in bHaptics Developer Portal
app_name = "Hello, bHaptics!"
# Initialize SDK
result = await bhaptics_python.registry_and_initialize(app_id, api_key, app_name)
print(f"Initialization result: {result}")
asyncio.run(main())
close
async def bhaptics_python.close()
Close the SDK connection.
Status Checking
is_playing_event_by_request_id
async def bhaptics_python.is_playing_event_by_request_id(request_id: int) -> bool
Checks the playback status of a specific request ID. Works whether event-based, or direct playing.
is_playing_event_by_event_id
async def bhaptics_python.is_playing_event_by_event_id(event_name: str) -> bool
Checks the playback status of a specific event.
is_playing_event
async def bhaptics_python.is_playing_event() -> bool
Checks the overall haptic playback status. Works whether event-based, or direct playing.
is_bhaptics_device_connected
async def bhaptics_python.is_bhaptics_device_connected(position: int) -> bool
Checks the connection status of a device at a specific position.
Parameters
position: Type of haptic device to check.Value Device 0TactSuit 1TactSleeve(Left) 2TactSleeve(Right) 3TactVisor 4Tactosy for Hands(Left) 5Tactosy for Hands(Right) 6Tactosy for Feet(Left) 7Tactosy for Feet(Right) 8TactGlove(Left) 9TactGlove(Right)
Example
import bhaptics_python
# Check connection status for all positions
async def check_all_positions_example():
for i in range(10):
is_device_connected = await bhaptics_python.is_bhaptics_device_connected(i)
print(f"Position {i} device connection: {is_device_connected}")
Device Control
Device Control functions allow you to manage and interact with connected haptic devices directly, such as pinging, setting vibration strength, or swapping device positions.
ping
async def bhaptics_python.ping(device_address: str)
Sends a ping to a specific device.
Parameters
device_address: The MAC address of the haptic device. Obtain the address usingget_device_info_json.
Example
import bhaptics_python
import json
async def ping_first_device_example():
device_info_string = await bhaptics_python.get_device_info_json()
device_info_list = json.loads(device_info_string)
if len(device_info_list) > 0:
bhaptics_python.ping(device_info_list[0]['address'])
ping_all
async def bhaptics_python.ping_all()
Send a ping to all connected devices.
set_device_vsm
async def bhaptics_python.set_device_vsm(device_address: str, value: int)
Sets the VSM (Vibration Strength Multiplier) value for a device.
Parameters
device_address: The MAC address of the haptic device. Obtain the address usingget_device_info_json.value: VSM (Vibration Strength Multiplier) value. The default VSM is100(x1.00 Feedback Intensity). Valid range is: [0-200]
Example
import bhaptics_python
import json
async def set_first_device_esm_example():
device_info_string = await bhaptics_python.get_device_info_json()
device_info_list = json.loads(device_info_string)
if len(device_info_list) > 0:
bhaptics_python.set_device_vsm(device_info_list[0]['address'], 100)
swap_position
async def bhaptics_python.swap_position(device_address: str)
Swaps the position of the device between left and right.
The devices that can swap the position are:
- Tactosy for Feet
- Tactosy for Hands
Parameters
device_address: The MAC address of the haptic device. Obtain the address usingget_device_info_json.
Example
import bhaptics_python
import json
async def swap_first_device_example():
device_info_string = await bhaptics_python.get_device_info_json()
device_info_list = json.loads(device_info_string)
if len(device_info_list) > 0:
# Swap the position of the first device
await bhaptics_python.swap_position(device_info_list[0]['address'])
Information Retrieval
get_device_info_json
await bhaptics_python.get_device_info_json() -> str
Return connected device information in JSON format.
Returns
The string that contains device information in JSON format.
This is an example of a returned string when two haptic devices are connected in an environment.
[
{
"position": 0,
"deviceName": "TactSuitPro",
"address": "UNIQUE_ADDRESS_GOES_HERE",
"connected": true,
"paired": true,
"battery": 72,
"audioJackIn": false,
"vsm": 20
},
{
"position": 3,
"deviceName": "TactVisor",
"address": "UNIQUE_ADDRESS_GOES_HERE",
"connected": true,
"paired": true,
"battery": 85,
"audioJackIn": false,
"vsm": 20
}
]
Example
import bhaptics_python
import json
async def device_count_example():
device_info_string = await bhaptics_python.get_device_info_json()
device_info_list = json.loads(device_info_string)
print(f"Connected device count: {len(device_info_list)}")